Why do ecommerce businesses fail?
A recent research study of failed e-commerce businesses found that 37% cited poor online marketing, while 35% listed a lack of online search visibility.
That’s consistent with our own research, which found that attracting more customers is one of the biggest challenges for NZ Ecommerce businesses.
That’s why we’ve launched a new training course all about Ecommerce Marketing.
Demand for online shopping has really ramped up following Covid-19, but that doesn’t necessarily make it any easier to attract buyers for your products.
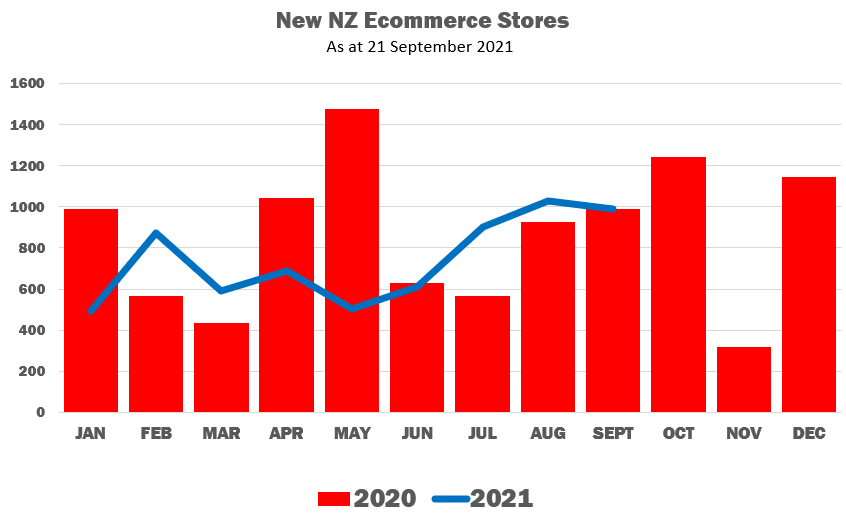
There are more buyers, but also many more sellers — over 21.000 new NZ ecommerce stores since the beginning of 2020, according to records compiled by the NZ Ecommerce Association.
According to research by NZ Post, 305,000 adult New Zealanders shopped online for the first time during 2020. That’s a healthy dose of new prospects for your products — but you still need to market to them if you want to attract them to your store.
And marketing to consumers is more challenging than ever.
These days, consumers search for products across a variety of media (not just Google Search). They are also searching on Facebook, YouTube, Amazon, Trade Me, TheMarket and a zillion other places. They ask for recommendations on YouTube, Instagram, WhatsApp, Facebook, Snapchat and other social outlets. They read reviews and ask their friends and whanau for validation before clicking “add to cart”.
The good news is that the New Zealand economy has stood up surprisingly well so far and consumers are still spending online at record levels.
However, in tougher times like these, many consumers take longer to decide on purchases and need more information to ensure that they are spending wisely. Oh, and wherever possible they’re looking for deals and discounts — or, at least, great value.
So how do you attract more customers?
Our online course, ECOMMERCE MARKETING, tells you what you need to know in a ten-part programme that steps you through the principles and practices of marketing your New Zealand ecommerce store.
The course has been created for Netmarketing Courses by Michael Carney, longtime marketer and author of the top-selling book “Trade Me Success Secrets” (now in its Second Edition) which tells how to sell effectively on this country’s largest and most successful eCommerce platform. Michael is also the creator of a number of other online courses (including several Social Media Marketing courses) and consults on many digital business initiatives.
This is an online course, conducted on a web-based e-learning software platform, enabling course participants to proceed at their own pace, anytime 24/7, accessing materials online.
This particular online training course provides content in a variety of multimedia forms, including videos, slideshows and PDF files. No special software is required to participate: you simply access the course through a web browser, on desktop or mobile devices.
Course lessons will be provided in ten parts, for participants to access in accordance with their own timetables.
WHO SHOULD TAKE THIS COURSE
Any Ecommerce Store operator who wants to attract more customers and close more sales.
CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
Here’s what some of our students have said about our Mastering eCommerce course:
- Really informative course, definitely helping us whilst we start out on our first ecomm project in NZ — Rob. T
- Thanks for another great course. I found it insightful, in-depth and I know our web presence and web sales will improve because of it. — Bruce H.
- I have somehow managed to develop over 80 pages of my own notes to complement the course ones. I look forward to participating in another in the near future. — Mark J
COURSE CONTENT
Course Content for ECOMMERCE MARKETING includes:
Introduction
We start by examining today’s ecommerce environment.
With the coronavirus-induced lockdown in March 2020, suddenly far more Kiwis discovered the joys of shopping online. During Level Four, when we could only purchase essential products, online shopping demand went through the roof.
As time moved on, we saw that many consumers switched their buying intentions back to bricks and mortar shopping — but online shopping remained at higher levels than in previous years, with purchases from domestic shopping websites up 34% versus June 2019:

Source: Marketview
That trend has continued, throughout 2020 and 2021.
But Kiwi businesses are facing more online competition than ever.
Today, we find ourselves facing competition from more and more online stores and from traditional bricks & mortar stores as well.
So how are YOU expecting to attract more customers in this environment?
Lesson One: Create Sizzling Product Listings
The first step in attracting more customers begins with your website.
It would be tempting to think that all you have to do is toss your products onto a website, with a few attractive images and a brief description, and your job is done.
Alas, the reality is otherwise. In this lesson, we discuss the fact that to serve up your product listings to potential customers, Google needs words that match the keywords and keyword phrases for which people are searching. That’s your first priority.
Those words also need to be compelling to humans, because if you can’t convince them that your product will meet their needs then you’ve just wasted the time and effort you put into attracting them to your product listing page.
But wait, there’s more. You also need gorgeous photographs that show off all the features and benefits of your products, because when customers can’t inspect your goods in person, they need to be able to properly check them out online.
Oh, and if there is any complexity about your product and how to use it, a video showing off its various attributes has really become a must-have in today’s environment.
In Lesson One, we also talk about:
- the vital importance of the headline
- what matters most to consumers when deciding whether or not to buy your product
- what makes a great product image
- the five big questions that should shape your offer
- 11 types of irresistible offers that you should consider
Lesson Two: Understand Your Customers
No matter what you’re selling, the key to your success is understanding your prospective customer. If you don’t understand what makes them tick, what their needs are and what they want, how can you serve them effectively?
In this lesson, we discuss ten things you need to know about your customers, including:
- Who they are (age range, gender, location)
- What they do (their interests and their online behaviours)
- Why they buy
- When they buy
- How they buy
- How much money consumers have (especially post-Covid)
- What makes consumers feel good about buying
- What they expect of you
- What they think about you
- What they think about your competitors
Lesson Three: Master Google Organic Search
We made the point in Lesson One that search engines need useful text descriptions so that they can understand your website. Turns out that there’s quite a science to being found online (and an industry has grown up around the challenges of what’s now known as Search Engine Optimisation, SEO). In essence, if you want your prospects to find your web pages, those pages need to contain content that prospects are looking for.
Not only that, but each page also needs to be structured effectively to take advantage of the (current) requirements of Google and its AI-powered algorithms.
In this lesson, we’ll be exploring the key functionality of Google Search, along with advanced capabilities of which you should attempt to take advantage, including:
- what BERT when it comes to organic search results
- why and how zero-click searches can be both deadly problems and great opportunities
- how Voice Search is transforming the ways in which consumers gather information, and how that in turn requires a whole new approach to keyword optimisation
- what you need to know about Topic Clusters, to ensure your priority placement in search engine results
- the opportunities (and problems) inherent in Featured Snippets
- how keyword search is giving way to User Intent as the most meaningful search signal
- the dramatic growth in Natural Language Search
- the increasing importance of structured data as Google uses AI more and more to handle search results
- why E-A-T (Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness) is now an essential content metric
- the convergence of SEO and Content
- why speed is now vital to your search success
- how Location, Location, Location is now a search engine mantra as well
Lesson Four: Optimise Paid Search
Not every page can be Number One on Google. So if you want to hit the top of the search engine rankings (especially for the most popular search phrases), sometimes you have to pay. In this lesson, we talk in detail about Google Ads and other Pay Per Click advertising tools.
We discuss long-tail keywords and share tools to help you understand exactly how to compile lists of keywords and keyword phrases for your advertising.
And we’ll also be exploring these key topics and strategies:
- Use SKAGs (Single Keyword Ad Groups) for your ad campaigns
- Use extensions for more dominance
- Always Be Testing: test your ad copy 24/7
- Go beyond Google Ads (check out Bing, etc.)
- Create dedicated campaigns for voice searches
- Should you really focus on being #1?
- Measure. Measure. Measure.
Lesson Five: Leverage Google Shopping
It has long been essential to be well represented on Google Search, using appropriate keywords on your webpages.
More recently, however, Google has introduced its own Google Shopping facility. If consumers search for a particular product by name, advertisers can pay to offer their products directly on the Google search results page.
According to Search Engine Land, Shopping ads account for roughly 75% of clicks from non-branded product searches. All queries considered—branded and non-branded—Shopping ads drive around 52% of ecommerce advertisers’ clicks. Elsewhere, Smart Insights reports that American ecommerce vendors who advertise on Google drive 85% of their paid clicks from Shopping ads.
In this lesson, we explore:
- How Google Shopping works
- Setting campaign priorities
- Tracking conversions from Google Shopping campaigns
- Using negative keywords
- Ensuring that your product listings meet Google’s data feed quality standards
Lesson Six: Master Social Media Advertising
You probably already have a business page on Facebook and perhaps even an account on Instagram. If your audience is predominantly female, you may well be using Pinterest to showcase your products. Maybe you’re even dabbling with the hottest social medium of the year (at least for teenagers), TikTok.
But if you’re not paying to advertise on your preferred social medium, you really won’t be getting much traction. The social networks are commercial enterprises and advertising is how they make money. So they’ve dialled back dramatically on the amount of content they will share with your followers.
Want to reach the people who’ve liked your page? Mostly, you’ll have to pay.
In this lesson we introduce you to the principles and practices of social media advertising, and take you on a tour through Facebook Ads Manager (which is the tool that some six million advertisers use to advertise on both Facebook and Instagram). We also discuss:
- why you shouldn’t just boost your posts and expect to get effective results
- the key differences between Google Adwords and Facebook Ads and why they matter to you
- the limitations faced by New Zealand advertisers compared with our foreign counterparts
- how (if you’re not careful) you can end up competing with yourself and drive up your social advertising costs
- an analysis of the New Zealand Facebook & Instagram marketplaces
- why mobile is so important (and why that matters to you)
Lesson Seven: Just Add Video
Online Video is a powerful way to communicate your brand story, explain your value proposition, and build relationships with your customers and prospects. This lesson introduces you to the basic principles and explores some of the available tools.
Not all videos are created equal, however, and we look at the demand for Vertical Videos (thanks, Instagram), Square Videos (preferred by the social networks), Outstream Videos and other permutations and combinations now on offer.
Along the way, we’ll discuss:
- the implications of the new reality that videos are replacing photos as the primary way we create and share memories
- how AI and the use of closed captions are making video content more searchable
- videos are getting shorter (because consumers are quick to skip)
- videos are getting longer (as more longform entertainment content is made available online, especially via Facebook Watch and IGTV)
Lesson Eight: Involve Influencers & Influentials
If you are new to the world of ecommerce, and don’t already have a substantial following, then you might consider reaching out to influencers and influentials to help you connect with prospective customers.
We have deliberately differentiated between the labels “influencer” and “influential”, largely as a result of the arrival of Internet-based influencers, whose voices can be heard across social media platforms such as Instagram and YouTube.
By our definition, those are “influencers” whilst the more traditional “influentials” tend to be found amongst the likes of journalists, neighbourhood leaders, industry analysts, business networkers and academics.
Both influencers and influentials could potentially have a place in your marketing, depending upon your product category and/or the types of consumers to whom your products appeal.
Why involve influencers or influentials? Because, according to a report by Nielsen, 92% of people trust recommendations from individuals over brands. And, let’s face it, many brands have brought that fate upon themselves by their own less-than-trustworthy behaviour.
In this lesson, we consider the importance of Influencer Marketing — and explore how to identify effective Kiwi micro-influencers who will be good ambassadors for your brand.
Lesson Nine: Maximise Email Opportunities
In Lesson Nine, we turn our attention to that perennial marketing mechanism for online retailers, email.
As HubSpot notes:
Despite the amazing advancements in social media and on-site user interface design for communicating with customers, email is still one of the best tactics eCommerce marketing professionals can use to leverage prospects and past customers to increase eCommerce sales.
Email is popular because it still works. According to the US Direct Marketing Association’s Power of Direct economic impact study, email marketing is currently the top performing marketing channel in terms of return on investment (ROI), with a projected return of US$39.40 for every dollar spent.
In this lesson, we:
- explore the sixteen key elements of an effective email programme for eCommerce operators
- discuss key legislation that impacts on the use of email (including the Unsolicited Electronic Messages Act and the new 2020 Privacy Act)
- ponder the power of personalisation
- consider marketing automation as a viable tool
Lesson Ten: Accelerate Through Remarketing
Remarketing is one of the most powerful tools in the ecommerce operator’s arsenal.
So what exactly is Remarketing? Here’s how Webopedia defines the term:
Remarketing refers to the techniques, strategies and often the automated email systems used by marketers and online merchants to follow up with Web site visitors who do not make a desired action on the Web site—usually when they abandon their shopping cart.
Think of it like this: you market to bring a visitor to your website, and if he or she doesn’t make a purchase, you then use remarketing tactics to bring the visitor back to your website and convert him or her in to a paying customer.
In this lesson, we talk about:
- the power of remarketing
- remarketing through email
- remarketing through Facebook
- remarketing through Google
- best practices to maximise profit and improve conversion rates
Conclusion
We review what we’ve covered and suggest strategies to implement relevant learnings.
TIMING
This course begins on Thursday 05 March, 2026
[ifso id=”6241″]
If you would prefer to pay by bank deposit, or require an invoice before making payment, please send an email to info@ecommerce.org.nz with details of your request.
(The service provider will be shown as Netmarketing Courses in your transaction and on your credit card statement).
WHAT HAPPENS NEXT?
Your booking will be confirmed by email (if you have not received a confirmation within 24 hours, feel free to email info@ecommerce.org.nz .
On the first day of the course you will be supplied by email with login details and Course Notes for Lesson One.